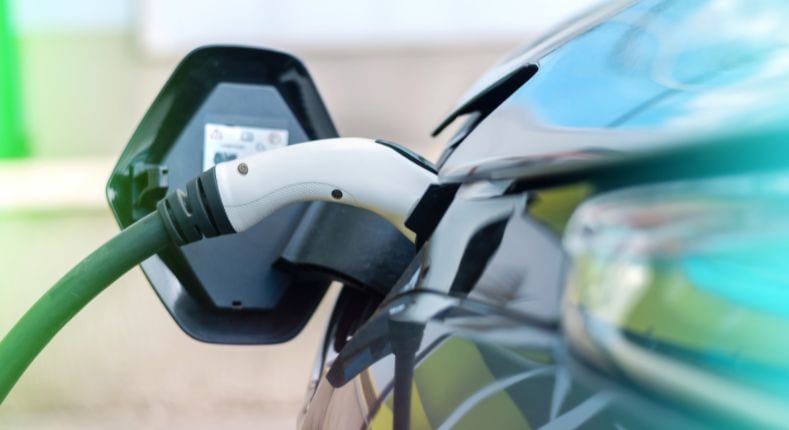
In recent years, we have witnessed an unprecedented transformation in the way we travel. The electric car revolution not only promises cleaner and more efficient mobility, but also presents challenges and opportunities in the area of electric car charging.
In this context, electric vehicle charging emerges as one of the key pillars to ensure the viability and sustainability of future transport. But how do we ensure that this drive for greener mobility does not end up being simply a shift from dependence on one type of energy to another, equally problematic one?
The answer shines on us every day: the sun. Clean, inexhaustible and increasingly accessible, solar energy is emerging as the ideal solution to power the growing fleet of electric vehicles. Integrating solar energy into the charging ecosystem not only reduces our carbon footprint, but also brings us closer to real and sustainable energy autonomy.
With a view to the future, where sustainability is more than an option, it is a necessity, we invite you to immerse yourself in the world of solar electric vehicle charging. Together, we can take a giant step towards a cleaner, more efficient and sustainable future.
Understanding the Types of Electric Vehicle Chargers
The world of electric vehicles is as diverse as it is innovative, offering a variety of options to meet the charging needs of different users. Understanding the types of chargers available is key to maximising the efficiency of your electric vehicle and tailoring your charging routine to your daily needs. Below, we explore the main types of chargers you’ll find on the market:
Slow Charging or Domestic
Slow charging, also known as home charging, is the most accessible and easiest way to start charging your electric vehicle. Using a standard household socket (Schuko socket in Europe), this type of charging offers a power output of up to 3.7 kW. Although it is the least fast option, allowing the vehicle to be fully charged in approximately 8 hours, it represents a practical solution for users who can charge their vehicle overnight at home.
Semi-fast loading
This method increases the charging speed using alternating current, either in single-phase (up to 7.4 kW) or three-phase (11 kW or 22 kW) mode, which significantly reduces the charging time to less than 3 hours for a full charge in the case of the most powerful installations. It is ideal for workplaces or public car parks where vehicles are parked for several hours.
Fast and Super Fast Charging
Fast charging, which uses direct current, offers charging power of up to 50 kW, allowing more than half of the battery to be charged in just 30 minutes. On the other hand, super-fast and ultra-fast charging, still in the experimental phase for many vehicles except for some high-end models, such as those from Tesla, can offer charging powers of up to 150 kW or more, reducing charging time to just a few minutes. These chargers are especially useful for long journeys, where charging time is a critical factor.
Each type of charger has its place in the electric vehicle ecosystem, from the convenience of overnight charging at home to the speed needed at public charging stations on long journeys. Choosing the right charger will depend on your specific needs, the capacity of your vehicle’s battery, and the availability of charging infrastructure in your area.
Types of Connectors and Their Importance
The efficiency and safety of charging an electric vehicle depends not only on the power of the charger, but also on the type of connector used. The connector is the physical bridge between the charging point and the vehicle, and its compatibility is essential for successful charging. Let’s examine the main types of connectors on the market and their importance:
Schuko plug
The Schuko plug is the standard domestic socket in many European countries. Although it is the most accessible for slow or domestic charging, its use is limited by the slower charging speed it offers and, in some cases, the electrical safety of the domestic installation.
Type 1 (SAE J1772)
The Type 1 connector is a standard mainly used in America and Asia for alternating current (AC) charging. It allows safe charging up to approximately 7.4 kW, making it suitable for domestic or semi-fast charging.
Type 2 (Mennekes)
The Type 2, or Mennekes, connector is the predominant standard in Europe. Its design supports both AC charging (for slow and semi-fast charging) and DC charging (for fast charging), offering wide versatility and compatibility with a range of charging powers up to 43 kW in AC and even more in DC.
CCS Connector (Combo 2)
The Combined Charging System (CCS) integrates AC and DC charging functionality in a single connector. It is the preferred type for fast and ultra-fast charging, supporting charging powers up to several hundred kW, making it ideal for public charging stations and long journeys.
CHAdeMO
CHAdeMO is a DC fast charging standard originating in Japan. Although it has been widely used, especially in Japanese vehicles, its presence is gradually being overtaken by more integrated solutions such as CCS in many regions.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Connector
Choosing the right connector not only ensures that you can charge your vehicle efficiently, but also affects the safety of charging. Vehicles and charging points are often compatible with various types of connectors, offering flexibility to users. However, knowing the capabilities and limitations of each type of connector can help you make informed decisions about where and how to charge your electric vehicle, especially when planning long journeys or considering installing a charging point at home.
With a clear understanding of the types of chargers and connectors, we are ready to explore how solar energy can revolutionise electric vehicle charging, taking sustainability to a new level.
The Synergy between Solar Energy and Electric Vehicle Charging
In a world rapidly moving towards sustainability, solar energy is emerging as a key pillar in powering electric vehicles. This section breaks down how integrating solar photovoltaic systems with electric vehicle charging infrastructure is not only possible, but also incredibly beneficial.
Solar Energy: An Abundant and Clean Resource
Solar energy, captured through photovoltaic panels, represents an inexhaustible and clean source of electricity. By converting sunlight directly into electricity, solar panels offer a carbon-free way to generate energy, significantly reducing the carbon footprint associated with electric vehicle charging.
Integration of Solar Systems with Electric Vehicle Chargers
The integration of solar systems into electric vehicle charging infrastructure can be realised in a variety of ways, from residential solutions to large-scale installations:
- At Home: Homeowners can install solar panels on their roofs to generate enough electricity not only for their domestic needs, but also to charge their electric vehicles. This “solar-to-vehicle” solution turns homes into self-contained mini power plants, maximising energy independence.
- In Businesses and Public Spaces: For businesses and public administrations, installing solar charging stations for electric vehicles in car parks and public access spaces offers a double advantage: it promotes sustainable mobility and demonstrates a commitment to renewable energy.
Benefits of Solar Electric Vehicle Charging
- Reduced Emissions: By powering electric vehicles with solar energy, dependence on fossil fuels is eliminated, bringing us closer to a completely green mobility cycle.
- Cost-effectiveness: In the long term, the initial investment in solar panels is offset by savings in electricity costs, making solar charging an economically attractive option.
- Energy Resilience: Point-of-use power generation decreases dependence on the grid, providing a more stable and reliable source of energy.
Success Stories and Future Potential
Around the world, there are numerous examples of how solar electric vehicle charging is already being successfully implemented. From residential communities to corporations and local governments, the momentum towards integrating solar energy into electric vehicle charging is palpable. These cases not only demonstrate the technical feasibility of such systems, but also illustrate the potential for massive expansion in the coming years.
Frequently Asked Questions about electric car chargers:
Are there bi-directional electric chargers?
Yes, bi-directional technology allows the EV to charge and discharge, making it possible to use it as an energy storage unit to replace or augment household energy capacity. Your electric vehicle can serve as a power source for the household or even bring the energy back to the grid (depending on the power company).
Do I have to register another supply point in order to install a charging point for the electric vehicle?
It will not be necessary to register a new supply point, you will only have one bill for the consumption of the home and the charger. Depending on the contracted power and the type of charging point you wish to install, it may be necessary to increase the power.
Can I plug the electric vehicle into a normal household socket?
It is not at all safe to charge your vehicle from a normal electrical socket. Charging your electric car from a normal electrical outlet raises serious safety concerns. Normal electrical sockets and cables are not designed to charge at high capacity for a long period of time.
Does the electric vehicle charge on a cloudy day?
This depends on the type of solar panel installation chosen. Here we distinguish between 2 types:
Isolated installation: it is totally disconnected from the electricity grid. It works by accumulating solar energy in batteries and is normally associated with a slower recharging process.
The self-consumption installation: it is connected to the electricity grid. It supplies our recharging point with the electricity needed to recharge the vehicle. This supply is carried out in real time and the energy will depend on the photovoltaic capacities of the self-consumption installation. The surplus energy that may be available after recharging the vehicle is transmitted to the home’s electricity grid, which means a saving in electricity both in terms of economic and environmental costs.
How much power does an electric vehicle need?
One point to take into account is to know the number of panels needed and therefore the power. It depends on the consumption of the household and the vehicle. It usually ranges from 13.2 kWh for a plug-in hybrid to 50 kWh for a 100% electric car.
For example: if we have an electric vehicle with a 50 kWh battery and we drive, on average, around 15,000 kilometres per year, we will need 2,205 kWh to recharge it. And to produce that energy we would need 5 solar panels that could generate 450 kWh of energy each.
Can I charge my electric vehicle at night?
Most drivers who have an electric vehicle in their private garage use night time to recharge it, but as you can imagine, a photovoltaic installation does not generate energy during that period of time. Therefore, it would be ideal to carry out this process during the day, when the panels will be operating at full capacity.
For this reason, opting for a connected installation is a great decision, as you take advantage of the cheaper night-time tariff and add the financial compensation from the supplier for the surplus energy you have generated during the day.
Is it possible to charge an electric vehicle at home with solar panels?
And it would be the most sustainable combination to use the electricity generated by your solar panels to charge your electric vehicle.
The philosophy of sustainable mobility consists precisely in travelling with an electric vehicle that does not directly generate local emissions and whose energy is obtained from a renewable source, such as the sun.
Take the plunge and calculate your potential savings today and be amazed by the economic and environmental advantages that solar self-consumption has in store for you. At SolarMente, we’re here to accompany you every step of the way on this exciting journey towards a greener, more economically sustainable future – start making a positive change now!