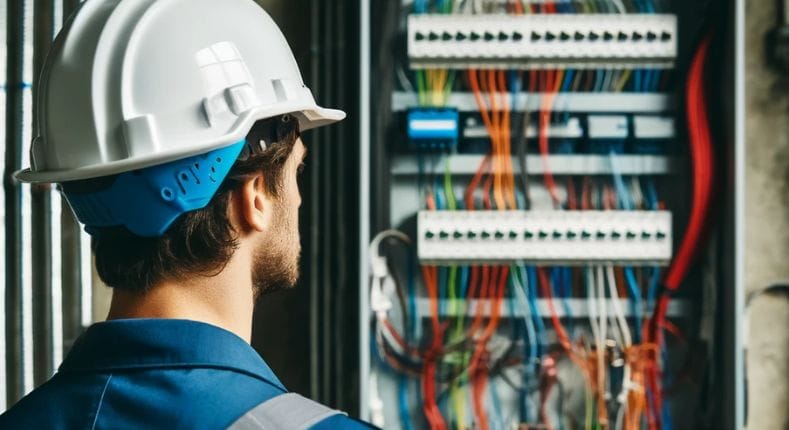
In this post, we will explore in detail what single-phase and three-phase installations are, their typical applications, and how to choose between one and the other.
Through practical examples, frequently asked questions and a visual guide, we will provide you with all the tools you need to understand and make the best decision regarding the electrical installation in your home or business.
What is a Single Phase Installation?
A single-phase installation is a type of electrical configuration that uses a single phase of alternating current to distribute electricity. This simplicity makes it ideal for residential and small business applications where power demands are not excessively high.
In this type of installation, electricity flows through two main cables: one that carries the current (phase) and one that serves as a return (neutral). In some cases, it may include a third wire, the earth wire, which helps to protect the system and the users against possible electric shocks.
Main characteristics of single-phase installations:
- Standard Voltage: In most countries, single-phase installations operate on voltages that can vary between 220 and 230 volts, suitable for most household appliances and electronic equipment.
- Power: The usual contracted power for these systems is up to 3.7 kW, which is sufficient for the energy needs of an average household without high consumption equipment.
- Simplicity and Cost: Because they use less wiring and equipment, these installations are easier and cheaper to install and maintain than more complex systems.
Advantages of single-phase installation:
- Cost-effectiveness: They are generally cheaper to install and maintain.
- Sufficient for domestic uses: Adequately provides the energy needed for common household appliances such as refrigerators, televisions, computers and lights.
- Ease of installation and repair: As a simpler system, electrical problems are easier to diagnose and repair.
Disadvantages:
- Power limitations: Not suitable for properties or operations requiring higher energies, such as large industrial machines or intensive central heating systems.
- Lower efficiency in large spaces: In very large buildings, it may not be sufficient to cover all energy needs efficiently.
Next, we will explore the three-phase installation, which is used when power demands exceed the capabilities of a single-phase installation, especially in commercial or industrial contexts.
What is a three-phase installation?
A three-phase installation is an electrical configuration that uses three different alternating currents, each 120 degrees out of phase with respect to the others, to distribute electricity.
This type of installation is commonly used in industrial and large commercial environments, where energy demand is significantly higher than in residences.
Main characteristics of three-phase installations:
- Standard Voltage: Three-phase installations typically operate at voltages from 380 to 400 volts, which allows them to handle much higher loads compared to single-phase installations.
- Power: Capable of supplying power in excess of 15 kW, these installations are ideal for powering heavy industrial equipment and large air conditioning or heating systems.
- Load Distribution: Three-phase distribution allows for a more balanced load along the three phase cables, which improves efficiency and reduces the likelihood of voltage sags and overloads.
Advantages of three-phase installation:
- Increased energy efficiency: By operating with three phases, these installations can distribute more power with less energy loss.
- Stability: Balanced load distribution across all three phases reduces voltage fluctuations, which is critical in environments where sensitive and expensive machines are used.
- Flexibility in handling high-performance equipment: Able to simultaneously handle multiple power-hungry devices without compromising performance.
Disadvantages:
- Higher initial and maintenance costs: Due to their complexity, three-phase installations require a higher initial investment as well as higher maintenance costs.
- Technical complexity: Requires a deeper understanding for installation, operation and maintenance, often involving the need for specialised technicians.
These installations are preferred in contexts where efficiency and the ability to handle large loads are critical, such as in factories, large workshops or buildings housing multiple businesses with high energy requirements.
By understanding the capabilities and requirements of single-phase and three-phase installations, property owners and managers can make informed decisions about the electrical infrastructure that best suits their needs.
Comparison between single-phase and three-phase systems
In order to facilitate the understanding of the fundamental differences between single-phase and three-phase installations, below is a comparative table highlighting their main characteristics, uses, advantages and disadvantages:
| Feature | Single-phase | Three-phase |
| Standard Voltage | 220-230 volts | 380-400 volts |
| Power | Up to 3.7 kW (suitable for homes and small businesses) | Above 15 kW (ideal for industries and large buildings) |
| Load Distribution | A single phase distributes the entire load | Three phases allow for a more balanced and efficient distribution |
| Installation and Maintenance Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to its complexity |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower compared to three-phase due to power limitation | Higher, with better energy utilisation and lower energy loss |
| Stability | Less stable, may have more voltage fluctuations | More stable, with less fluctuations due to balanced distribution |
| Common Applications | Households, small shops, offices with low energy requirements | Factories, large shops, buildings with high energy demand |
| Technical Complexity | Low, easy to install and maintain | High, requires specialised technicians and is more costly to maintain |
| Space requirements | Less space for electricity infrastructure | Requires more space for panels and additional equipment |
This table summarises the main considerations when deciding between a single-phase and a three-phase installation. The choice between one or the other will depend on a number of factors, including the specific energy needs of the site, the available budget and the future requirements for scalability and adaptability of the electrical installation.
Integration of Solar Energy with Single-phase and Three-phase Installations
The adoption of solar energy is crucial for sustainability and energy efficiency. Depending on whether the installation is single-phase or three-phase, the integration of solar PV systems varies in complexity and cost.
Solar energy with single-phase installation:
- Simplicity of Integration: Suitable for homes with moderate energy demands.
- Cost-efficiency: Less expensive, no need for additional components.
- Self-sufficiency: Possibility of adding batteries for energy storage.
- Challenges: Limited by power capacity; may require adjustments if consumption increases.
Solar energy with three-phase installation:
- Increased Capacity and Efficiency: Ideal for large properties or businesses with high daytime consumption.
- Balanced Distribution: Improves system stability and efficiency.
- Large System Optimisation: Facilitates advanced energy management.
- Challenges: Higher initial cost due to additional components such as three-phase inverters.
Choice Considerations:
- Energy Needs Assessment: Crucial to determine the right type of installation.
- Professional Consultancy: Recommended for effective and personalised planning.
- Local Regulations and Subsidies: Important to understand the economic viability of the project.
Integrating solar energy is both a green decision and a strategic investment that brings long-term economic and environmental benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions on the Choice between Single or Three Phase Power in a Household
Here are some frequently asked questions that may arise when deciding whether to install single-phase or three-phase power in a home, along with detailed answers to help homeowners make an informed decision:
1. What type of electrical installation is most common in dwellings?
Most households use single-phase installations because they provide enough power for standard household appliances and general day-to-day use. This type of installation is less expensive and simpler to maintain.
2. In which cases would it be appropriate to opt for a three-phase installation in a dwelling?
A three-phase installation may be suitable for very large homes with high energy demands, such as those with multiple central air conditioning systems, large workshops with machinery, or any equipment requiring more than 10 kW of power. It is also recommended for homes that use intensive electric heating systems or multiple high-consumption appliances simultaneously.
3. Is it more expensive to install three-phase power than single-phase power?
Yes, installing three-phase power is generally more expensive than single-phase due to the need for additional wiring, a more complex electrical panel, and possibly more installation work. In addition, maintenance can be more technical and costly.
4. Can I switch from a single-phase to a three-phase installation if my energy needs increase?
Yes, it is possible to switch from a single-phase to a three-phase installation, but this involves a complete overhaul of the existing electrical system, including the panel, the wiring and, in some cases, even the electrical supply. This process can be costly and is only recommended if it is really necessary to meet the energy needs.
5. What is involved in the maintenance of a three-phase installation compared to a single-phase installation?
Maintenance of a three-phase installation can be more complex due to its multi-phase configuration. This requires a more advanced knowledge of electrical systems and may require more frequent professional intervention to ensure that all phases are balanced and functioning correctly.
6. How do I know if my home needs a single-phase or three-phase installation?
Ideally, consult a professional who can assess the total energy needs of the home based on the appliances and equipment being used. The professional can perform load calculations to determine if a single-phase installation is sufficient or if it would be beneficial to opt for a three-phase installation.
These questions and answers can serve as a useful guide for homeowners considering their electrical installation options, helping them to make decisions based on their actual needs and available budget.
Discover your savings potential today and marvel at the economic and ecological benefits of solar self-consumption.
At SolarMente, we are committed to guiding you through every phase of this exciting journey towards a more sustainable and economically viable future. Don’t wait any longer to start making a positive impact on the world and your life – take the first step towards meaningful transformation and join our solar community now!